Recognizing an implant abscess early can be a lifesaver for your dental implant. Timely intervention can safeguard your oral health and prolong the implant’s longevity. Read on to learn the vital information needed for a successful and safe implant procedure.
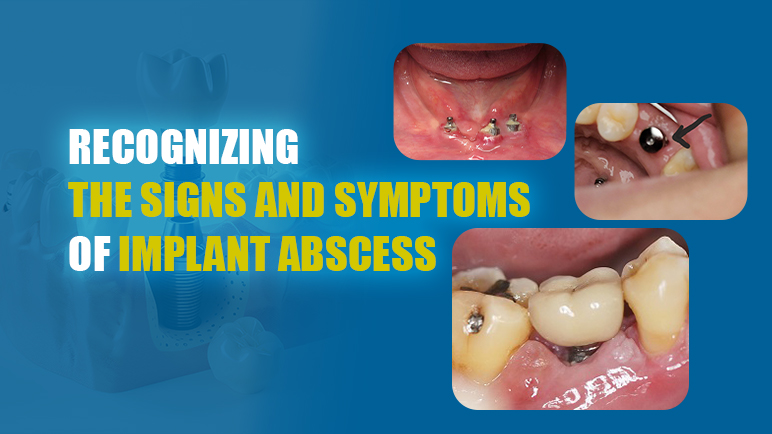
What is an implant abscess?
Dental implant placement is a surgical procedure involving the insertion of a titanium post into the jawbone, serving as a root for a missing tooth. This method boasts a success rate of up to 98%, enabling patients to restore both chewing function and aesthetics to a level comparable to natural teeth. So, can dental implants get infected?
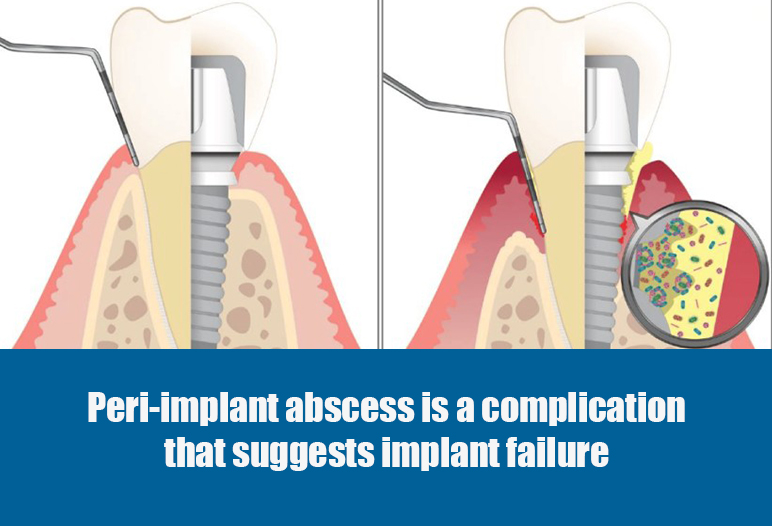
In reality, dental implant infection symptoms can still occur due to various factors. Dental implant abscess is a classic symptom of failed implant placement. An implant abscess develops when bacteria invade the tissue surrounding the implant, causing local inflammation. The body’s immune response attempts to combat this invasion, leading to the formation of pus. This infected area can cause significant discomfort and swelling, and if left untreated, may compromise the stability of the implant.
Signs of a Tooth Implant Infection
A tooth implant infection can be a serious issue if not treated quickly. Timely diagnosis of an infected implant can prevent further deterioration and severe complications. Being aware of the common signs and symptoms associated with implant abscesses aids in early intervention. Below are some common signs to watch out for if you suspect your dental implant is infected:
Pain and swelling around the implant
Pain is often the first noticeable symptom of an implant abscess. The intensity of pain can range from mild discomfort to severe throbbing that radiates to adjacent areas of the jaw and face. Many individuals report that the pain can intensify during the night or when lying down.
Swelling also typically accompanies pain, appearing either localized around the implant or extending to larger areas of the jaw or cheek. Facial swelling can sometimes indicate a more serious infection that requires prompt medical attention. The manifestation of pain and swelling should never be overlooked, as they serve as crucial indicators of an underlying issue that might require immediate intervention.
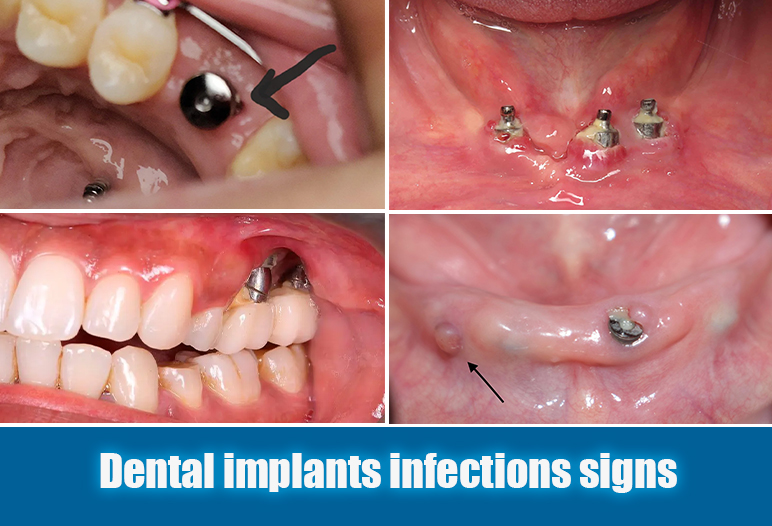
Swollen gum around implant
Inflammation, and dental implant pus are other telltale signs of an implant abscess. The skin and gums surrounding the implant may exhibit redness and tenderness, suggestive of infection. Patients may notice an unusual discharge of pus from the affected area, which can vary in color and consistency.
Discharge may possess an unpleasant odor due to bacterial byproducts. The presence of pus and its characteristics provide insight into the severity of the infection. Noticing these symptoms should prompt patients to seek dental advice immediately to avoid the progression of the infection.
Bad taste or odor in the mouth
Tooth implant infection symptoms can alter taste and smell, leading to chronic bad breath. Many patients describe a foul or metallic taste, attributed to toxins and bacterial byproducts present during the infection process.
If individuals notice persistent bad breath, despite consistent oral hygiene practices, it’s essential to investigate further. This symptom often correlates with deeper issues, such as an ongoing infection that demands professional evaluation and intervention.
Can dental implants become infected? If you experience any dental implants infections signs, it’s important to see a dentist right away.
Causes of implant abscesses
Several factors contribute to the development of implant abscesses. Understanding these causes helps identify potential risk factors associated with individual patients and promotes proactive management strategies.
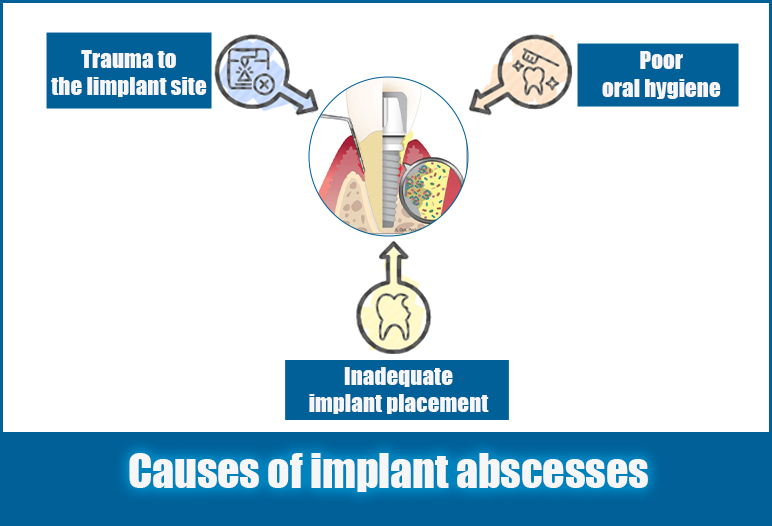
Poor oral hygiene
Poor oral hygiene can lead to an abscess around a dental implant. When oral care is neglected, plaque and bacteria accumulate around the implant, creating an environment that allows bacteria to thrive, which can cause infections and eventually result in an abscess.
An implant abscess occurs when bacteria infiltrate the tissues surrounding the implant, leading to inflammation and pus formation. If left untreated, this condition can cause swelling, and pain, and potentially compromise the stability of the implant.
Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, is essential in preventing such infections and keeping the implant healthy.
Trauma to the Iimplant site
Physical trauma introduces another risk factor contributing to tooth implant infection.
Various forms of trauma can compromise the integrity of the tissues surrounding the implant, allowing bacteria easy access to the site.
- Accidental biting: Biting down on hard objects or clenching your teeth inadvertently can inflict injury to the delicate tissues encircling the implant.
- Physical injuries: Falls, sports accidents, or other impacts can directly damage the implant and surrounding structures.
- Dental procedures: Sometimes dental treatments, such as scaling, can unintentionally cause injury, creating openings that can lead to infection.
These traumatic events create opportunities for bacteria to invade, leading to the possibility of an abscess forming around the implant.
Understanding how trauma influences implant health helps patients take steps to limit risks, such as wearing protective mouthguards during physical activities or being cautious about grinding teeth.
Inadequate implant placement
The success of a dental implant heavily relies on its proper integration with the surrounding bone, known as osseointegration. During the surgical process, precise positioning is critical. If an implant is inadequately placed, it may fail to integrate properly with the bone.
Improper placement creates a gap between the implant and the bone, providing a secluded area where bacteria can thrive, leading to an infected dental implant. When bacteria invade, it can result in the formation of dental implant pus, causing pain and discomfort.
Additionally, if bone grafts or sinus lifts are not adequately integrated, it can further complicate the situation, increasing the risk of infection.
Diagnosing an implant abscess
Early diagnosis of an implant abscess is vital for determining effective treatment strategies. Dentists utilize various methods to evaluate the condition of the implant and surrounding tissues.
Clinical examination
A comprehensive clinical examination serves as the preliminary step in diagnosing an implant abscess. Dentists visually inspect the implant site for visible signs of infection, including redness, swelling, tenderness, and discharge. They may also palpate the area to assess the extent of discomfort and swelling.
This examination provides initial insights into the severity and location of the infection, enabling dentists to form a preliminary diagnosis. However, given the limitations of visual inspection alone, further diagnostic measures are often necessary.
Radiographic imaging
Can a tooth implant get infected? Dental radiographs can be utilized to detect early signs of implant infection. Radiographs, such as panoramic X-rays, offer valuable insights into the state of the implant and surrounding bone structures. These images help identify any bone loss around the implant, which may indicate a more established infection.
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) represents an advanced imaging technique utilized for detailed visualization. CBCT enables three-dimensional representation of the implant and its relationship with adjacent bone, assisting in accurately assessing the extent of the infection. This level of detail is invaluable for guiding treatment decisions and planning appropriate interventions.
Detailed dental implant infection pictures obtained through specialized examinations allow dentists to provide timely and effective treatment. This enables you to protect your oral health, preserve your implant, and avoid the need for reimplantation
Laboratory tests
In specific cases, laboratory tests may facilitate further confirmation of the diagnosis. Obtaining samples of pus or discharge from the implant site allows for analysis to identify the specific bacteria responsible for the infection. This information assists dentists in determining the most effective antibiotics for treatment.
Blood tests may also be conducted to measure levels of inflammatory markers, providing additional insight into the patient’s overall health and the severity of the infection. This comprehensive approach ensures a targeted and effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
How to treat infection around dental implant?
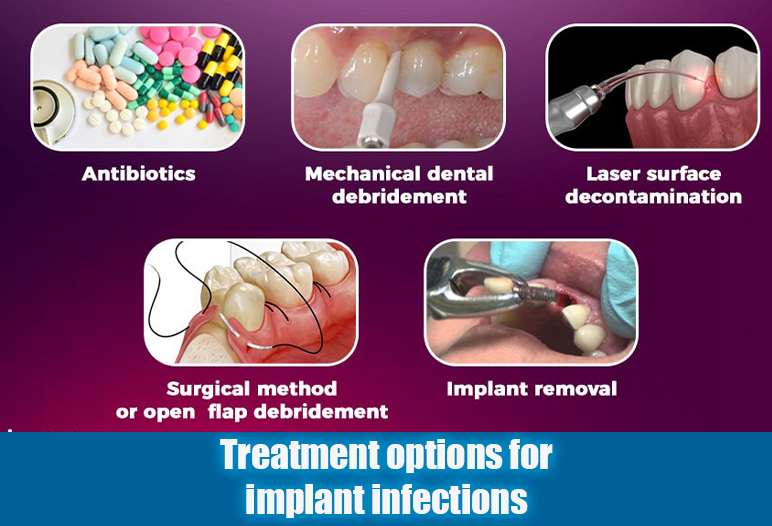
Once diagnosed, addressing an infected implant promptly is essential to minimize complications and promote healing. Treatment of dental implant infection options vary based on the severity of the infection, the state of the implant, and the patient’s overall health.
Antibiotics
How to treat dental implant infection? Antibiotics often represent the first line of defense against tooth implant abscesses. The dentist prescribes specific antibiotics based on the identified bacteria causing the infection.
These medications work to kill or inhibit bacterial growth, reducing inflammation and facilitating healing around the implant. Patients must follow their dentist’s instructions meticulously, completing the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is entirely eradicated.
Failing to adhere to prescribed antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistance or recurrence of the infection, underscoring the importance of compliance throughout the treatment process.
Tooth implant infection treatment: Surgical drainage
In instances where antibiotics alone prove insufficient, surgical drainage may be warranted. If the abscess has formed a significant pocket of pus, a small incision is made to drain the accumulated fluid. This procedure alleviates pressure and promotes healing.
Surgical drainage is typically performed under local anesthesia, allowing for a swift resolution of the discomfort associated with the abscess. Following drainage, careful monitoring and post-operative instructions are critical for fostering proper healing and minimizing the risk of recurrence.
Implant removal (in severe cases)
In severe situations where significant bone loss has occurred or the implant has become unstable, removal may be necessary. While the prospect of losing an implant is daunting, every effort aims to save the implant before resorting to this drastic measure.
Should removal be required, the area undergoes thorough cleaning and debridement to eliminate infected or necrotic tissue. A subsequent treatment plan will address the infection and consider long-term solutions, such as bone grafting or re-implantation, depending on the specific circumstances.
How to treat a dental implant infection at home?
Treating a dental implant infection at home requires careful management, but it’s important to consult with your dentist for professional advice. Here are some steps you can take at home to help manage a dental implant infection:
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Brush Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush, focusing gently around the implant area.
Floss Carefully: Use dental floss or interdental brushes to clean between teeth and around the implant, ensuring you do not irritate the area.
Rinse with Salt Water
Salt Water Rinse: Mix a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and use it as a mouth rinse several times a day. This can help reduce inflammation and cleanse the area.
Use Antimicrobial Mouthwash
Chlorhexidine Rinse: If recommended by your dentist, use an antimicrobial mouthwash like chlorhexidine to help kill bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
Pain Management: Take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, to manage pain and reduce inflammation. Follow the dosage instructions on the label.
Apply Cold Compress
Reduce Swelling: Apply a cold compress to the outside of your cheek for 15-20 minutes to help reduce swelling and discomfort.
Monitor Symptoms
Watch for Changes: Keep an eye on your symptoms. If pain, swelling, or discharge worsens, or if you develop a fever, contact your dentist immediately.
Avoid Certain Foods
Soft Foods Only: Stick to a soft diet and avoid hard, crunchy, or sticky foods that can irritate the implant site.

Stay Hydrated
Drink Plenty of Water: Keeping hydrated helps maintain good oral health and supports healing.
Preventing implant abscesses
Preventing an implant abscess is far more advantageous than addressing an infection after it occurs. Implementing simple yet effective measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing an abscess.
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is paramount in preventing infections related to dental implants. This encompasses several key practices:
- Brushing twice daily: Employ a soft-bristled toothbrush to gently clean the entire mouth while paying particular attention to the implant and surrounding tissues.
- Flossing daily: Utilize dental floss or interdental brushes to remove food particles and bacteria that may accumulate between the implants and natural teeth.
Diligent oral hygiene creates an unfavorable environment for harmful bacteria, minimizing the likelihood of infection and promoting optimal healing after implant placement.
Regular dental checkups
Routine dental checkups serve a dual purpose: ensuring ongoing oral health and monitoring the status of dental implants. Regular visits allow dentists to assess the condition of the implant and surrounding tissues, identifying potential issues before they escalate into serious complications.
Your dentist can provide personalized recommendations for maintaining oral hygiene, thus fostering a proactive approach to oral health. Establishing a schedule for regular checkups reinforces the importance of prevention and early intervention strategies.
Following Post-Surgical instructions carefully
After implant placement, adherence to post-surgical care instructions is essential to minimize complications. Patients should follow guidelines provided by their dentist, which may include pain management protocols, dietary restrictions, and specific instructions regarding oral hygiene.
Failure to comply with these instructions may jeopardize the success of the implant and increase susceptibility to infection. By prioritizing post-surgical care, patients can support proper healing and enhance the longevity of their dental implants.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of an implant abscess is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your dental implants and ensuring lasting oral health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options associated with implant abscesses, individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate risks and respond effectively to potential complications. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene, attending regular dental checkups, and actively following post-surgical instructions plays a pivotal role in preventing infections and preserving the success of your dental implants.
FAQs
How common is infection after dental implant?
Infection after dental implant placement is relatively uncommon, occurring in about 1-5% of cases. The risk can increase due to factors like poor oral hygiene, existing health conditions, and inadequate post-operative care.
How do I know if my post op dental implant infection?
You may suspect that your dental implant post is infected if you experience increased pain, swelling, redness, or discharge around the implant site. Other signs include a loose implant, persistent bad breath, or fever. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to contact your dentist promptly for evaluation and treatment.
What are the signs of bone infection from dental implant?
Here are some common signs of dental implant infection:
- Pain or discomfort: This can be a throbbing or aching sensation around the implant.
- Swelling: The area around the implant may become swollen or puffy.
- Redness: The gums around the implant may appear red or inflamed.
- Discharge: Pus or a foul-smelling discharge may come from the area around the implant.
- Bad breath: You may notice an unpleasant odor coming from your mouth.
- Loose implant: The implant may feel loose or wobbly.

 Google Reviews
Google Reviews Call
Call
SAIGON IMPLANT CENTER
Best dentist in Vietnam
Saigon Implant Center - Dental Clinic utilizes the latest technology for specialized treatment in the field of Single implant, full jaw implants, All on 4 implants, All on 6 implants, Zygoma implant....
SAIGON IMPLANT CENTER
Best dentist in Vietnam
Saigon Implant Center - Dental Clinic utilizes the latest technology for specialized treatment in the field of Single implant, full jaw implants, All on 4 implants, All on 6 implants, Zygoma implant....